The 2021 Fortune Global 500 and The Future of African Companies
Dec 23, 2021

INTRODUCTION
For 26 long years, being on the Fortune Global 500 list is seen as a sign of prestige and progress for the companies in it. The Fortune Global 500, commonly referred to as the Global 500 list, is an annual ranking of the world’s top 500 companies based on sales and revenue. Fortune magazine compiles and publishes the list every year.
In this comprehensive report, I would be doing some analytical research on the mutual characteristics of the FG500 companies, classifying and categorizing the different kinds of industries on the FG500. The report would also give insights on ways or methods African companies can get on the FG500 list. My list of 10 potential African companies to make the FG500 would be included alongside my reasons.
MUTUAL CHARACTERISTICS OF FG500 COMPANIES
The publication of the annual Fortune Global 500 list this year was welcomed with lots of anticipation and uncertainty as the Covid-19 virus caused a lot of shrinkage in the total revenue when compared to the 2020 list. The latest FG 500 survey has revealed that the U.S. and mainland China, including Hong Kong, once again dominate the Global 500 list. The U.S. ranked #1 in revenue with $9.7 trillion (-1.6% change from last year), and a #2 ranking in the number of companies (122). China ranked #2 with $8.92 trillion (+7.6%) in revenue and #1 in the number of companies (135).
Walmart remains unwavering at the number one spot for the 8th consecutive time while Rite Aid takes the last place on this list. Irrespective of their positions on the list, these companies have similar characteristics that earn them a place on the list. Some of these characteristics are discussed below.
HIGH REVENUES
Revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods or services related to the company's primary operations. Revenue figures include consolidated subsidiaries and reported revenues from discontinued operations but exclude excise taxes. For banks, revenue is the sum of gross interest income and gross noninterest income. For insurance companies, revenue includes premium and annuity income, investment income, realized capital gains or losses, and other income, but excludes deposits. So these companies despite their different industries i.e Retail, Technology, Banking etc generate huge revenue.
LARGE PROFIT
Profit describes the financial benefit realized when the revenue generated from a business activity exceeds the expenses, costs, and taxes involved in sustaining the activity in question. Profits are shown after taxes, extraordinary credits or charges, cumulative effects of accounting changes, and noncontrolling (minority) interests, but before preferred dividends. Revenue and profit figures for non-U.S. companies have been converted to U.S. dollars at the average exchange rate during each company’s fiscal year.
China still tops the list of having the most number of companies featured on the list. Some of the most profitable ones are China Construction Company, Agricultural Bank of China, Bank of China etc
SIZEABLE ASSET VALUE
An asset can be thought of as something that, in the future, can generate cash flow, reduce expenses, or improve sales, regardless of whether it's manufacturing equipment or a patent. Business assets are itemized and valued on the balance sheet. They are listed at historical cost and in order of liquidity. The companies under this list have earned their spot by accruing huge assets also.
For example, the State Grid Corporation of China- a Chinese owned electricity utility company as of 2017 had 585.3 billion USD which is humongous compared to a smaller company like Nestlé Nigeria that had in 2020 a total asset of 246,185,000 million naira ( $598,742 )
MACROSCALE EMPLOYEES
The figure shown is either a fiscal year-end or yearly average number, as published by the company. Where the breakdown between full- and part-time employees is supplied, a part-time employee is counted as one half of a full-time employee. The companies are large scale and as a result, obtain lots of employees.
These companies can afford to hire thousands of people and even provide them incentives, like the case of Xiaomi; in celebration of their inclusion to the FG500 list despite them being so young, they gave 20,000 employees free one thousand shares of the company. This was a total of 24 million dollars.
A SCHEMA TO CLASSIFY FORTUNE GLOBAL 500 COMPANIES
When examining all 500 companies on this Fortune Global list, because of how different and unique they are, it is easier to classify them into different categories for easy analysis. I would be using tools such as pie charts, bar charts, tables, diagrams and bullet points to illustrate these information.
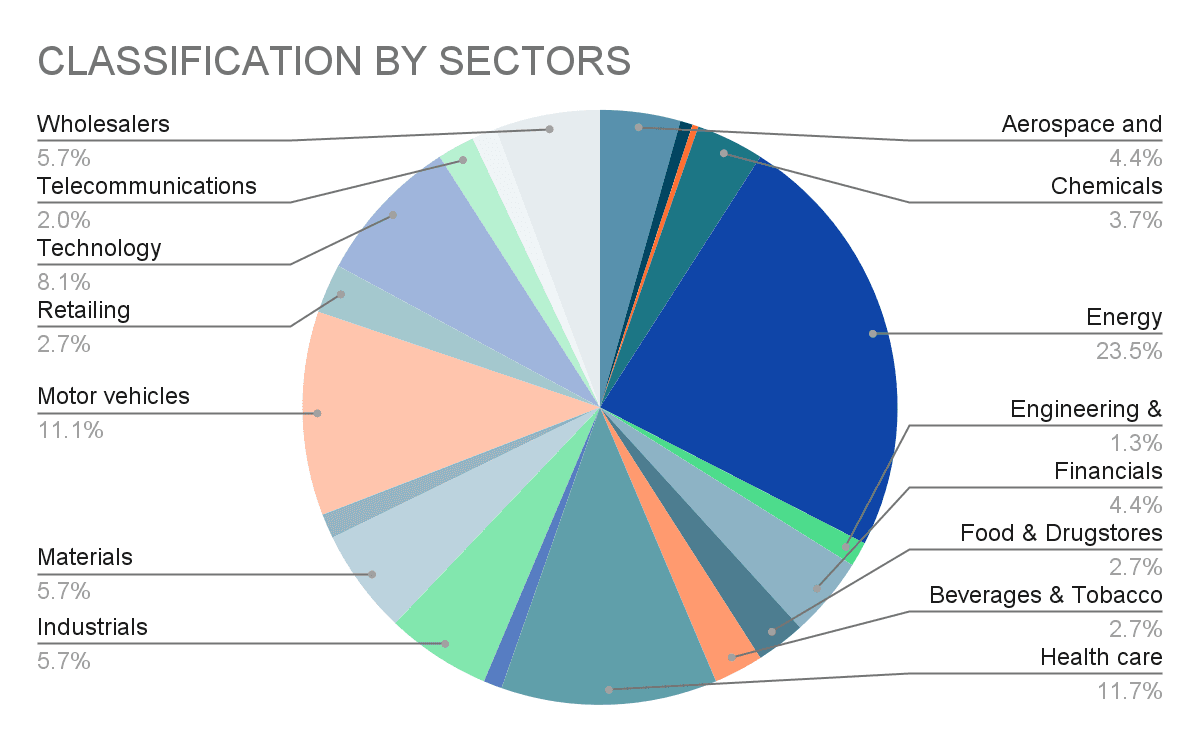
This carefully curated Pie chart clearly shows how the 500 companies are distributed across the 15 different sectors. Topping the chart is the Energy sector with 23.5%, with top companies like State Grid, China National Petroleum, Sinopec Group.
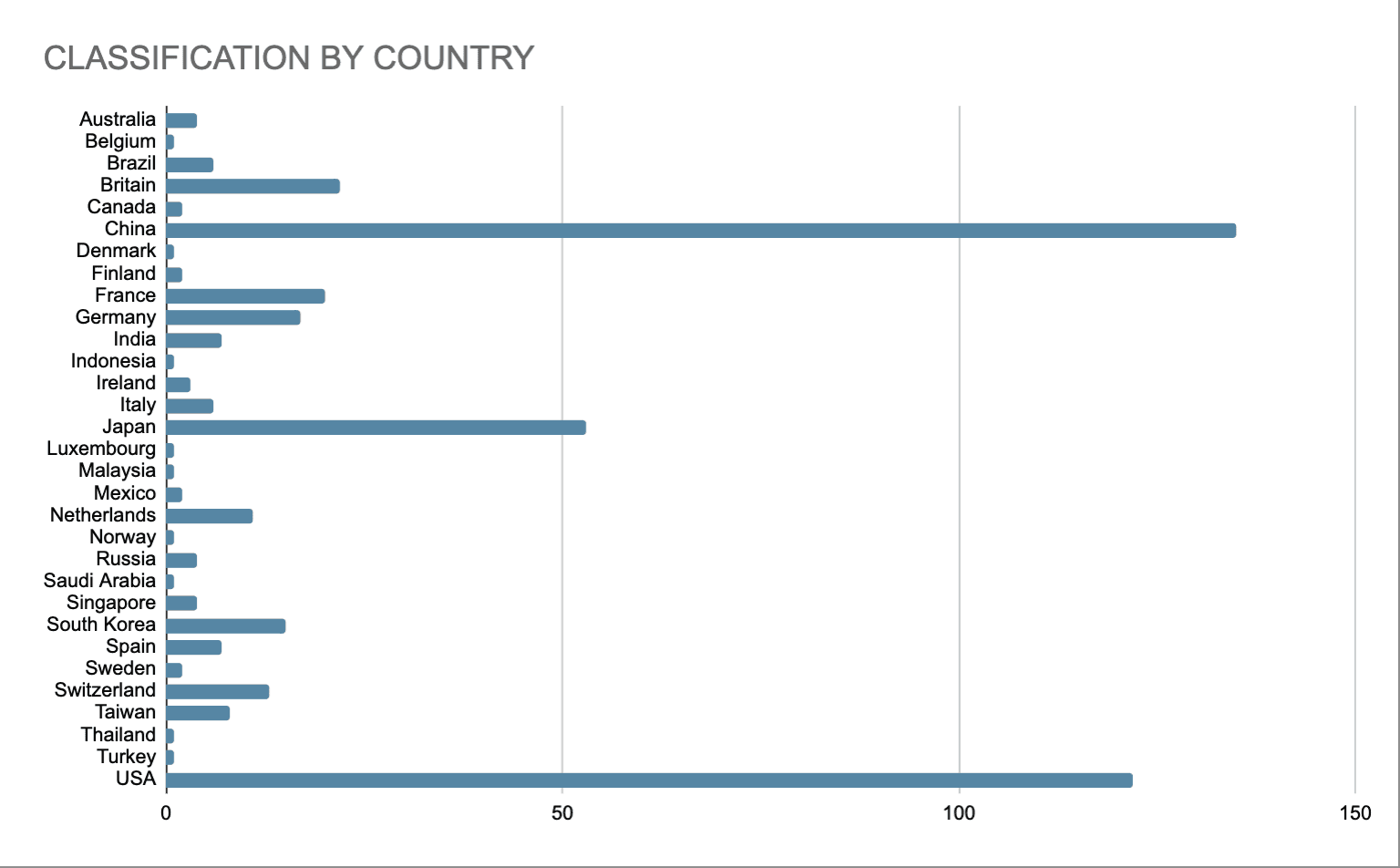
The next chart (bar) is created to show the distribution of these 500 companies around the globe. The number of companies based in North America has been on a decrease while Asian-based enterprises raised their contribution from 197 in 2017 to 207 in 2020 and now 211. The companies on the list for 2021 are located in 220 cities across 31 nations. The top 3 countries on the list as seen on the chart are China, USA and Japan.

For more insight, I would be classifying them by the most profitable. Below are the top ten profitable companies and they are not the same as top ten on the FG500 list, because other factors asides profit are included in the methodology.
Apple with profits of $57,411,000 and a total of 19 years on the FG500 list
Saudi Aramco with profits of $49,286,000 and a total of 3 years on the FG500 list.
SoftBank Group with profits of $47,052,000 and a total of 14 years on the FG500 list.
Industrial & Commercial bank of China with profits of $45,783,000 and a total of 23 years on the FG500 list.
Microsoft with profits of $44,281,000 and a total of 24 years on the FG500 list.
Berkshire Hathaway with profits of $42,521,000 and a total of 25 years on the FG500 list.
Alphabet with profits of $40,269,000 and a total of 13 years on the FG500 list.
China Construction Bank with profits of $39,282,000 and a total of 22 years on the FG500 list.
Agricultural Bank of China with profits of $31,293,000 and a total of 22 years on the FG500 list.
Meta Platforms with profits of $29,146,000 and a total of 5 years on the FG500 list.
Proceeding to the least profitable company on the 2021 FG500 list is Heraeus Holdings, despite appearing 9 times on the list and having over 14,000 employees.
PROJECTING AFRICAN COMPANIES ON THE FG500 LIST
In the top 250 African companies currently, the Finance sector is taking the lead. In terms of Market Capitalization by region South African companies have a great lead with over $526,228,000. Despite her largeness in landmass, population, resources African companies are yet to make or top the FG500 list. During the course of my extensive research, I found this information hard to grasp. This led me to prob most of these companies from different regions of Africa, check their growth, company policies, government policies and cite the problems or areas that need improvement.
Africa has some of the fastest-growing companies in the world but not even the growth by companies like Algeria's Sonatrach, Angola's Sonangol, MTN and the Bidvest Group could see them break into this year's list. In comparison, Asia or even China as a country can boast of over a hundred companies. Here is a look into why they are so successful we see that about 20 years ago China had only 8 companies on the list, that itself is a big win but nothing compared to where they are now. Along the line, China has provided a domestic market for enterprises to grow and puts continuous effort to expand domestic demands while in African countries especially West Africa the government have very little involvement in helping or expanding local demands.
China’s ascent as an economic domestic powerhouse is crucial to its ambition, its ambition to become the worlds biggest superpower. The government is doing this with a business plan that homegrown and less viable to global economic meltdown or shocks. It is important to highlight that African and Chinese economies and societies are quite dissimilar- Africa is majorly a Capitalist society while the latter is a Communist society. This shows why they are run so differently, most of the companies in China featured on the FG500 list are state-owned enterprises (SEOs) and the impact from the government and their policies proves why they are on top.
State-owned Enterprises (SOEs) can help international sellers quickly reach a large customer base however, working with an SOE can be much harder than expected. Advantages of a state-owned enterprise:
SOEs receive financial support from the government.
SOEs are known for receiving access to favourable policies such as:
Tax breaks on certain products
Lower interest rates on loans from state-owned banks
Access to a large and stable potential customer base.
Disadvantages of a state-owned enterprise:
Strict government control and restrictions around general operations and decision-making.
SOEs have a strong corporate culture and management tone.
Studies have shown that having a good work environment and cultivating positivity in the workplace pays huge intangible dividends that boost the company’s bottom line. Employees who love their jobs, enjoy their coworkers and look forward to the workday are more likely to do whatever they can to help the company thrive. A positive workplace culture affirms the value, dignity and worth of each employee, which benefits the individual and the organization. According to Harvard Business Review, cutthroat, competitive corporate cultures stymie productivity, whereas, supportive work environments create conditions for business growth. Workers who take pride in what they do and where they work want to see the company flourish. They ask what more they can do to help the company move forward. Highly motivated employees are goal-oriented and laser-focused on measurable results. They welcome high standards and push themselves to reach key performance indicators on schedule.
Positive work environment benefits include enhanced retention and recruitment of a diverse talent pool. In today’s postindustrial global economy, companies cannot expand their reach without the health of a diverse workforce. A company with a reputation of being a good place to work has an easier time attracting and keeping diverse talented employees. Forbes describes a positive workplace as one that is committed to equal opportunity and access to jobs and promotions, and where management consistently enforces policies prohibiting harassment, discrimination and bullying to support a positive working environment for all.
Great employer-employee relationship is instrumental to boosting the company’s growth and productivity. According to Inc. Magazine, in order to boost morale, it is vital to ensure your organization is structured clearly, has solid goals and focuses on well-being. This could mean evaluating the following:
Pay structure and benefits
Mission and vision
Opportunities for collaboration
Innovation programs
Wellness incentives
Appreciation awards and events
Community outreach
Communication
Opportunities to socialize and celebrate
Work-life balance
Leadership opportunities
Continuing education
If more leading African companies can embrace these changes, they would be able to ascend the economic global ladder and in about a decade or less the sought after FG500 list. Below is a list of my potential top 10 African countries to make FG500:
POTENTIAL AFRICAN COUNTRIES ON FG500 IN THE NEXT DECADE
NASPERS
Naspers has businesses and investments in Internet Technology based companies, eCommerce, Media and Entertainment. The headquarters is in South Africa. With a current world rank of 240 Nasper promises to exponential growth with the decade, its current Market Cap as at (Sep-01-2021) is 71.923 Billion USD
ANGLO AMERICAN PLATINUM
Anglo American Platinum Limited is the world's largest primary producer of platinum, accounting for about 38% of the world's annual supply and are based in South Africa. With a current world rank of 778 AAP is globally recognized, it has an Annual Revenue of 9,508 Million USD.
FIRST RAND
FirstRand is a Banking and Financial services company with headquarters is in South Africa. As of June 2020, FirstRand has 49,233 employees, 765 representation points, 6,598 ATMs. As of 2020, it has 111 Billion USD of total assets and 1.1 Billion USD of normalized earnings. It has a current world rank of 894 and was founded in the year 1998- over 20 years of experience and stability
ABSA BANK
Absa Bank, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Absa Group, offers a range of retail, business, wealth management, corporate and investment solutions to customers and clients across South Africa. As of 2020, it has 1,000 branches and 10,000 ATM's. It has a current world rank of 1,110.
MTN GROUP
MTN Group is a Mobile Telecommunication company. It offers voice, data and digital services to retail customers in the 21 countries in which operations have telecoms licenses and also offer enterprise solutions to corporate and public sector customers in a total of 23 countries. The headquarters is in South Africa. It has a current world rank of 1,277, they have grown by investing in sophisticated communication infrastructure, developing new technologies and harnessing the talents of our diverse team of people to now offer services to communities across Africa and the Middle East.
VODACOM GROUP
Vodacom Group is a telecom sector company providing voice, messaging, data and converged service, and investment holding company. The products of the company are mobile telephony and Internet services. The headquarters is in South Africa. It has a current world rank of 1,280 and Vodacom is majority-owned by Vodafone (60.5% holding), one of the world’s largest communications companies by revenue.
STANDARD BANK GROUP
The Standard Bank of South Africa Limited is a South African banking and financial services group. The benefit of Standard Bank Group is that it offers banking to small to medium institutions mainly to individuals. The company came into force in 1969 and its headquarter is in Johannesburg, South Africa. It has a current world rank of 1,329. They currently operate in 20 African countries.
CAPITEC BANK HOLDINGS
Capitec Bank is a Retail Bank Holding company. The headquarters is in South Africa. As of 2020, Capitec Bank has 14029 employees, 852 branches, 2380 ATMs and DNR, 6.7 Million digital clients, 13.8 million active clients. It has a current world rank of 1,394.
KUMBA IRON ORE
Kumba Iron Ore is an Iron Ore Operations mining company. It provides the raw materials to meet the growing consumer-driven demands of the world developed and maturing economies. The company is a responsible miner of diamonds, platinum and other precious metals, copper, nickel, iron ore and coal. The headquarters is in South Africa. In 2010, Kumba Iron Ore was one of the more successful divisions of Anglo American plc and it has a current world rank of 1,470
ITISSALAT AL-MAGHRIB(IAM)
ITISSALAT AL-MAGHRIB(IAM) is a regional telecommunications company. The products of the company are landline phones, mobile phone lines, fibre-optic internet, ADSL, 4G+. It offers solutions for individual customers, professionals and businesses, and its service portfolio includes mobile services, Internet and television services. The headquarters is in Morocco.
CONCLUSION
The world’s 500 largest companies generated $30 trillion in revenues and $1.9 trillion in profits in 2017. Together, this year’s Fortune Global 500 companies employ 67.7 million people worldwide and are represented by 33 countries. I cannot overemphasize the value of the FG500 and have discussed the other methodologies asides from the ranking by total revenue used to compile the list. It is indeed an interesting list, upon completion of my analytics I was able to determine what the mutual characteristics of the FG500 companies are.
Whilst developing a framework categorizing the different kinds of FG500 companies, I saw the distribution across countries, continents, industries and sectors, most profitable, fastest-growing etc. Also within this extensive research report are my observations on the current world rank of African companies and methods they can emulate to be on the FG500 list.
I am very positive that following this projection my list of 10 African companies would be a possibility and not just a mere dream.